
But as the management account, we have separated all the figures in order to bring a clear message to all departments. Sale departments must know about their target, production department needs to ensure that the variable cost must be within the control and the so on. Consequently, to achieve a profit of $125,000 after taxes, Adam Electronics needs to earn sales revenue of $156,250. This represents the gross profit, out of which taxes will be paid to arrive at the desired net profit.
Related AccountingTools Courses
In order to complete the target, the company needs to understand the relationship between variable cost, fixed cost, and selling price. Before achieving target net income, we need to hit the sale target, budgeted variable cost, and fixed cost. Target net income is the target profit that top management or shareholders set for the company to achieve in an accounting accounting articles and case studies for dummies period. At the beginning of the year, each company prepares the annual budget, which is the target for company to achieve during the year. We can not just set the target net income alone as it has a close relationship with sales, variable cost, and fixed cost. This analysis helps businesses determine the sales volume needed to achieve a specific target profit.
- Now, let’s check your understanding of calculating the target profit point.
- This method is particularly useful in scenarios where uncertainty is high, such as during economic downturns or when entering new markets.
- Analyzing the sales mix involves examining the contribution margin of each product and understanding how shifts in sales volumes affect overall profitability.
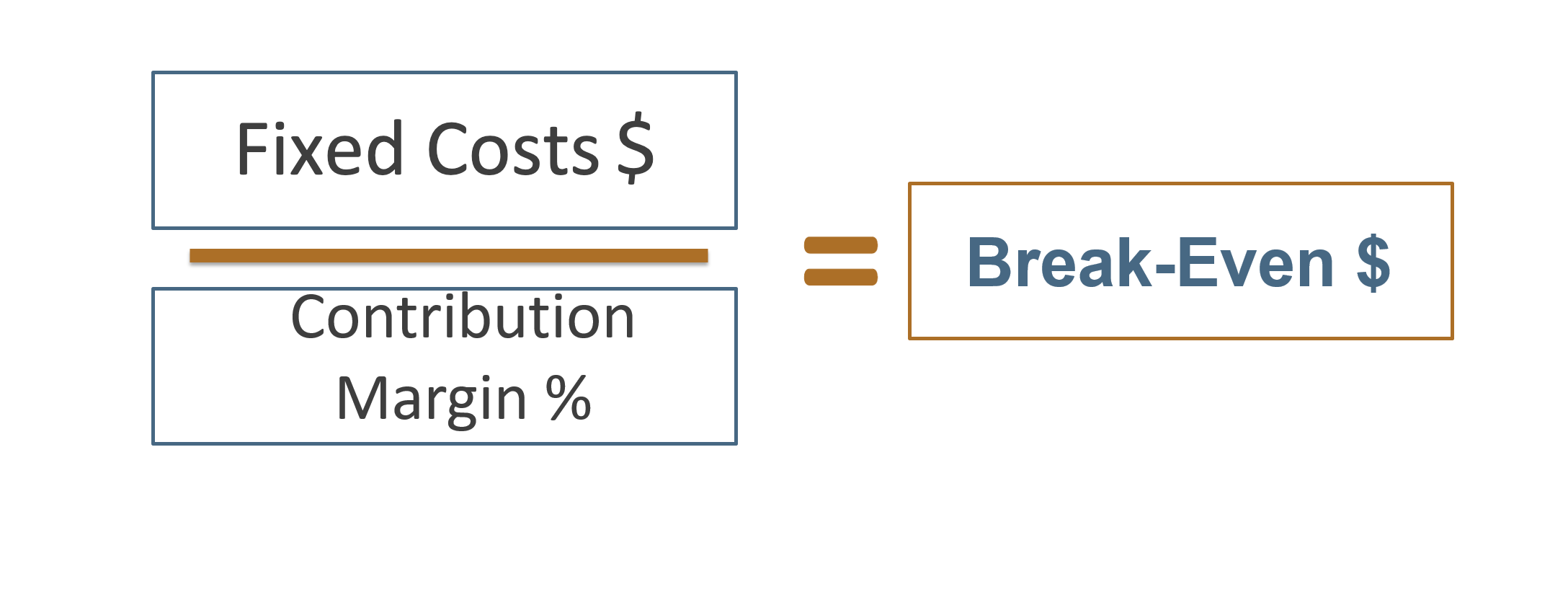
- Taking $100,000 and dividing it by the contribution margin ratio of 40%, this calculation yields a sales figure of $250,000.
7: Target Profit Analysis
They can decide where to cut expenses or when to invest more in marketing. Target net income is the best method which we use to make the connection between shareholder/top management and the other departments. Sale department will be notified about their target sale to support target profit. They can challenge back if it is too high and suggest any marketing strategy. Discover effective strategies and analysis techniques to achieve your target profit and optimize business performance.
Example 2 – Selling Price Unknown
Target profit is the desired profit that a business wants to achieve in an accounting or manufacturing period. The conventional approach is to set budgets and compare results against standards. No, calculating target profit isn’t hard if you know your costs and how much money you want to make. Knowing exactly how each dollar is spent clarifies where you can cut back or invest more. A firm grasp of target profit enables businesses to manage their revenue more effectively.
Target Profit Analysis:
This results in a reported variance between the actual and target profit figures, for which the accounting staff may provide a detailed explanation. However, budgets are notoriously inaccurate, and become more inaccurate the further into a budget year that you go. This tends to result in relatively small differences between the target and actual profit.
Managerial Accounting
One of the fundamental tools in assessing and achieving profit goals is target profit analysis. This analysis is particularly valuable for companies seeking to determine the level of sales needed to reach a specific profit target. As an illustration, suppose the business estimates the market in the first year will be 8,000 units and is has the production capacity to accommodate this. Additionally it decides that it can’t reduce the fixed costs or the production cost per unit, and needs to know the revised selling price to achieve the same target profit of 15,000. To find target sales revenue, divide fixed costs plus target profit by the contribution margin ratio.
Conversely, a shift towards low-margin products might necessitate a reevaluation of pricing strategies or cost structures to maintain profitability. This analysis helps businesses make informed decisions about which products to promote or phase out. Of course in practice it is not sufficient to simply amend one of the parameters.
The management can use the graphical method to calculate the break-even sales points as well as target profits for each product. This method uses the profit-volume relationship to calculate target profit. A common approach to achieving this desired profit is through the budgeting process. Knowing what target profit is sets the stage for understanding its role in business. Target profit acts like a compass for companies, guiding them towards financial success.
It involves not just setting financial goals but also implementing effective strategies and analysis techniques to meet these targets. Therefore, the business knows they need to keep fixed costs at £150,000 or under to attain their target profit. The business already knows their selling price is £150 per unit, their variable costs are £70 per unit and they expect to sell 5,000 units over the year.
Since each product typically has a different profit margin, the overall profitability can be significantly influenced by changes in the sales mix. For instance, a company that sells both high-margin and low-margin products will see its profit margins fluctuate based on the proportion of each sold. The business already knows their selling price is £500 per unit, their fixed costs are £2.5m per year and they expect to sell 10,000 units over the year. The management sets budgets for sales and costs to achieve a target profit.
This move clears up many calculation problems, leading you toward clearer financial success. Break-even analysis also aids in evaluating the impact of changes in costs, prices, and sales volumes on profitability. For example, if a company is considering a price increase, the analysis can show how many fewer units need to be sold to maintain the same profit level.





